Industry Thought Leadership
5G Deployment Models are Crystallizing
December, 20175G comes with the promise of unseen services and futuristic use cases. Telecom operators and other industry players are making big bets on next-generation services. With 5G, telecom operators can move away from being just connectivity providers to providers of new experiences and industry solutions.

5G will bring new interactive and immersive experiences to customers. Use cases are already being built around immersive sports viewing and augmented-reality applications. Beyond consumer applications, enterprises are actively investigating how they can benefit from 5G, and indeed thinking of deployment models themselves (e.g., smart manufacturing). We are also seeing whole industries organize themselves into ecosystems that would collectively benefit from 5G networks and related computing infrastructure (e.g., smart cities).
It is yet to be seen what role operators will play in these ecosystems, beyond facilitating their emergence, but some operators have already begun to shape the value chain and tune their services accordingly. For the first time, operators can play a key role in bringing corporates and industry verticals together, to deliver not just connectivity, but also solutions.

Meanwhile, 5G deployment models are crystallizing. New 5G pilots or technology updates are announced every month. We observe five distinct rollout models used by operators.
- Provide gigabit broadband to residential homes and an effective last-mile complement to existing fiber or cable networks. Verizon is actively announcing 5G based fixed broadband connectivity to selected cities in the USA.
- Deliver a next-generation, nationwide mobile experience that enables new use cases driven by virtual reality, tactile internet, etc. T-mobile is announcing 5G mobile rollout with its recently acquired 600 MHz spectrum.
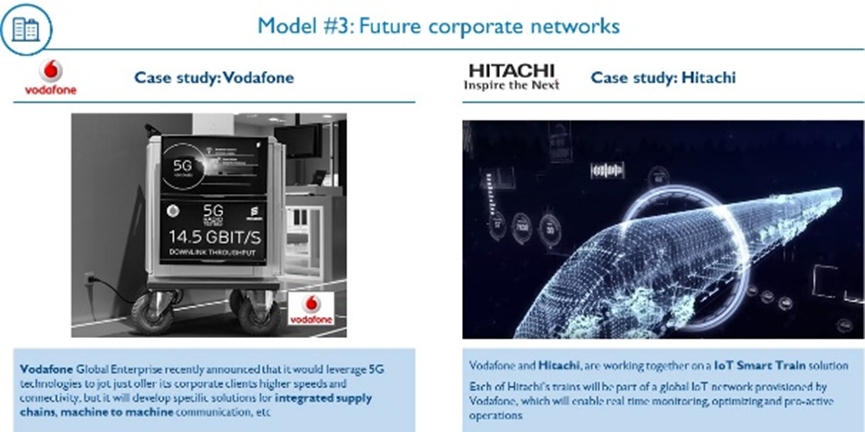
- Deliver highly reliable, low-latency connectivity and solutions, improving both efficiency and productivity for corporates. Vodafone is partnering with Hitachi to improve reliability and operations of its global fleet of passenger trains
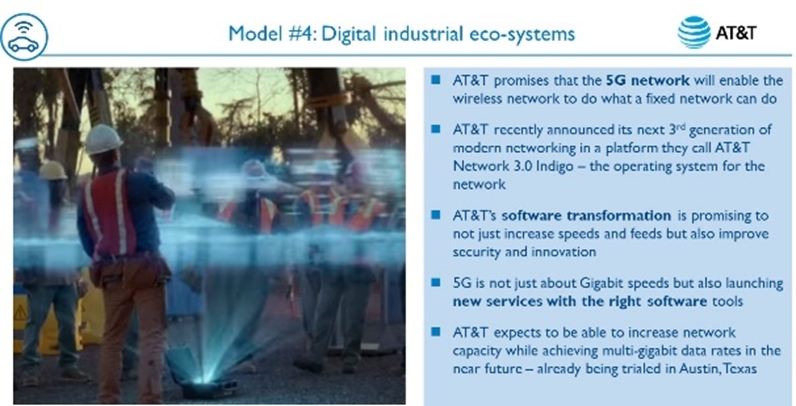
- Enable digital industrial ecosystems with machine-to-machine connectivity, facilitating new service ecosystems with multiple partners, providers and end users. AT&T recently announced its Network 3.0 Indigo which will use 5G and other technologies to enable its customers to launch gigabit services.
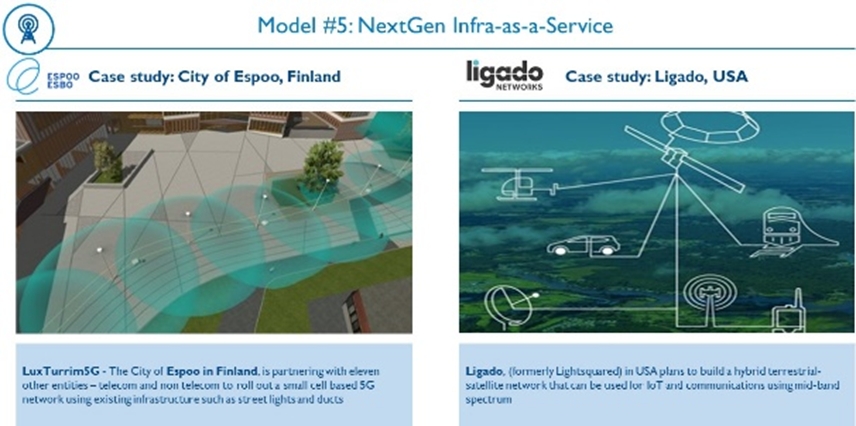
- Deliver next-generation infrastructure-as-a-service for the entire country. Cities, municipalities and non-telecom operators are entering the 5G infrastructure as a service space with neutral host solutions


Non-telecom players are already active in the 5G-enabled product space, with pilots in autonomous driving, virtual reality-based infotainment services and other use cases. If telecom operators don’t act fast, these new players will take an increasingly large share of this new ecosystem.

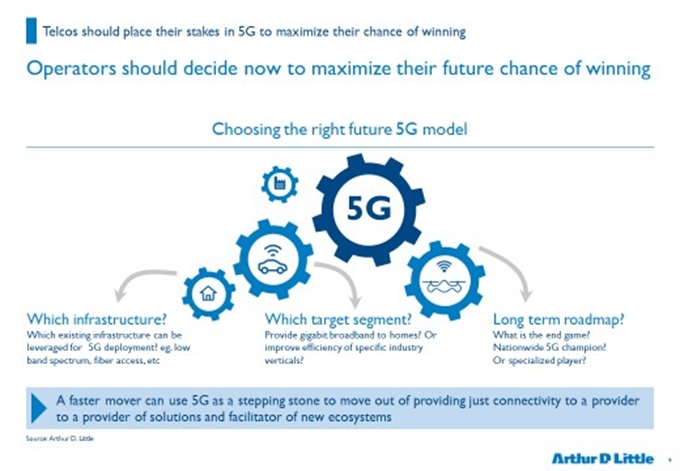
There are concrete steps that telecom operators can already take to place stakes in their 5G futures. Building an application ecosystem with start-ups and service providers, is key to facilitating future 5G use cases. Preparing the spectrum and infrastructure for future 5G macro and hundreds of thousands of small cells is another step that can be kick-started. Fiberization of fixed-access network, which will assist in aggregating and backhauling multi-gigabit traffic, as well as cloudifying the core to enable easy scale-up and external partnerships will eventually be required. Lastly, they will have to prepare their computing infrastructure to handle this gigabit traffic.
Telecom operators are approaching crossroads at which they must decide when and how to prepare for 5G deployment in a manner that will best suit their current market positions and future market needs. The five models described above are only a starting point for an operator planning to move towards 5G.
An operator might start with one model, and subsequently expand to other models or use a combination of models. In the future, non-telecom players such as Google, Apple and Amazon, which are active in the IoT space, might also join with 5G-based solutions of their own. Hence, it is important that telecom operators and vendors play an active role in driving the 5G standardizations in the right direction.
For further details, please download the entire report:
www.adl.com/5gdeployment

